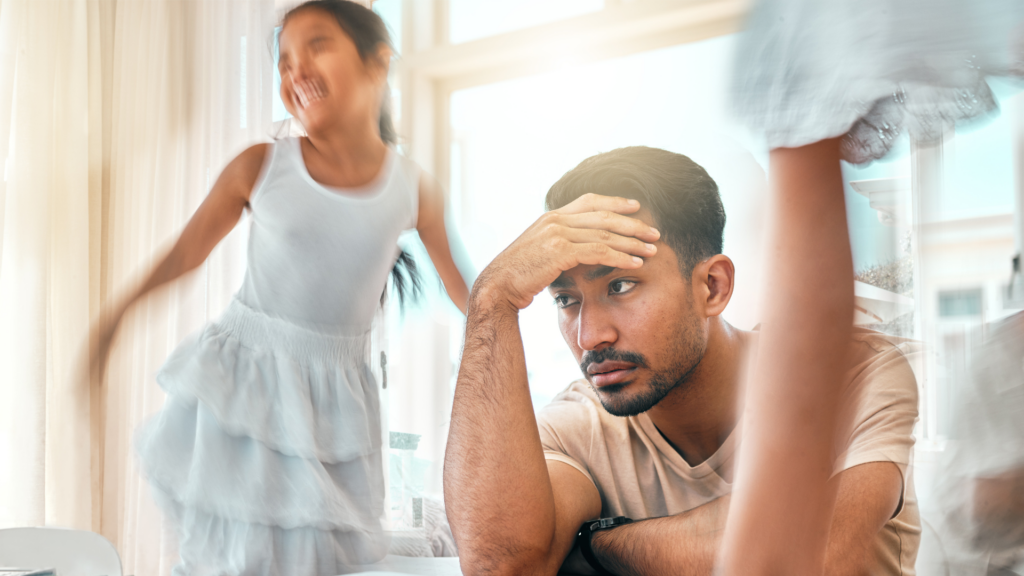
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are both neurodevelopmental conditions, and some individuals experience their combined effects. Such a condition is often referred to as AuDHD, which can present a unique set of challenges and symptoms. The dual diagnosis of ADHD and ASD makes the condition very complex (Mayes et al., 2012).
The first step to understanding AuDHD symptoms is to know what ADHD and ASD look like as separate conditions. AuDHD symptoms encompass traits from both conditions. Each individual's experience and symptom presentation will be unique and will require personalized support and understanding.
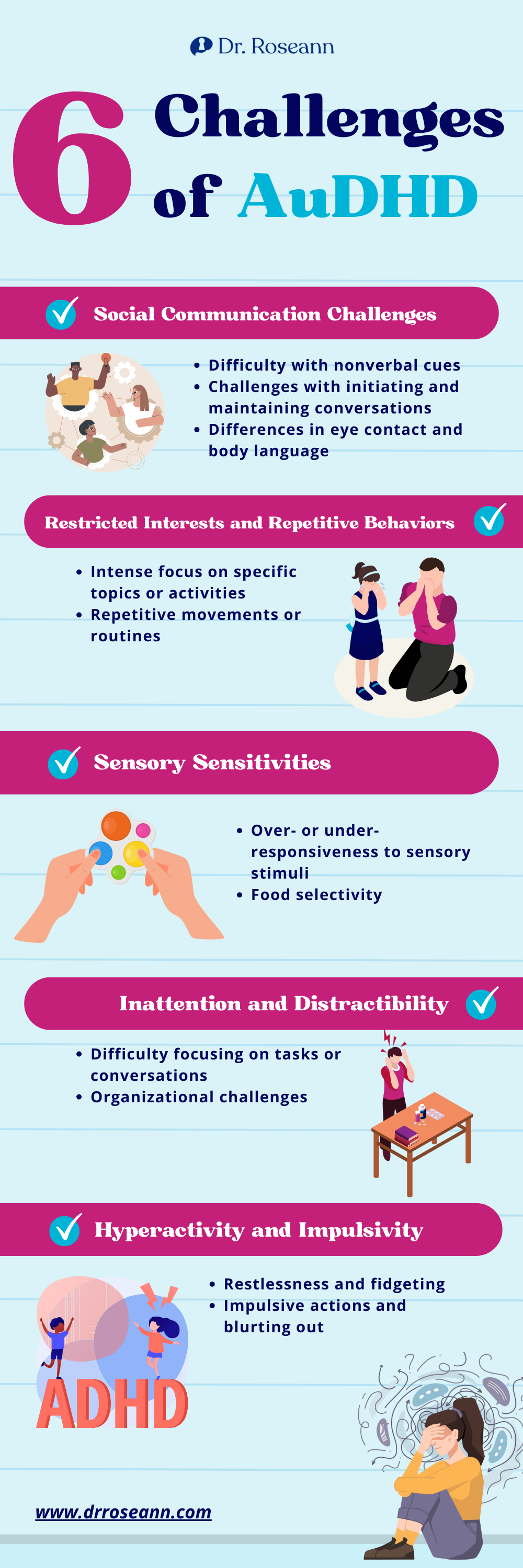
What are the Common AuDHD Symptoms?
The specific AuDHD symptom and its severity can vary significantly between children and teens with co-occurring ASD and ADHD. It's important to consult with a qualified professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate support tailored to the child’s unique needs and experiences (Grzadzinski et al., 2010). Here's a detailed explanation and example for each:
Distractibility
Kids with AuDHD may struggle with the symptoms of inattentiveness and distractibility. They're easily distracted by internal thoughts or external stimuli, just like most people with ADHD. These kids might also lose track of conversations and miss instructions. They also have difficulty focusing on tasks and paying attention, leading to academic or professional difficulties.
Example: Lisa struggles to concentrate in class due to the constant background noise of chatter and shuffling papers. She needs to wear noise-canceling headphones to focus.
Hyperactivity and Impulsivity
Hyperactivity can manifest as excessive fidgeting, restlessness, and difficulty sitting still. Impulsivity might involve blurting out answers, interrupting others, or acting without thinking, potentially causing social conflicts or risky behavior. These two are the most common symptoms of ADHD that are also evident in AuDHD.
Example: Because of Lucy's AuDHD, she can't easily control impulses. She often interrupts or intrudes on people in other groups, and blurts out the answer in class before the teacher finishes the question. This behavior often leads to frustration and classroom disruption.
Restricted Interests and Repetitive Behaviors
Managing impulses can be challenging for individuals with AuDHD. They might struggle to wait their turn, control their emotions, or resist engaging in repetitive behaviors. This can impact social interactions, daily activities, and emotional regulation.
Example: Susan has AuDHD and she performs a specific set of stretching exercises before the classroom and she feels anxious if this routine is disrupted.
Difficulties with Organization
Organizing tasks and activities can be a hurdle for individuals with AuDHD. They may face challenges with planning, time management, and keeping track of belongings, leading to missed deadlines, lost items, and cluttered environments.
Example: Johnny with AuDHD frequently misplaces his keys, phone, or homework due to forgetfulness and difficulties with time management.
Attention to Detail
While some individuals with ASD excel at focusing on minute details, others with AuDHD may struggle with focusing on specific points or maintaining sustained attention. This can impact learning, following instructions, and completing tasks that require accuracy.
Example: Johnny with AuDHD frequently misplaces their keys, phone, or homework due to forgetfulness and difficulties with time management.
Social Communication Challenges
Understanding and using nonverbal cues, initiating and maintaining conversations, and interpreting social rules can be complex for individuals with AuDHD. They might miss sarcasm, misunderstand facial expressions, and struggle with taking turns in conversation, which leads to social misunderstandings and difficulties in forming relationships.
Example: Brian struggling with AuDHD interprets a classmate's playful nudge as aggression and reacts defensively. This led to a misunderstanding between classmates.
Learning Disabilities
Some individuals with AuDHD may also experience learning disabilities alongside their core symptoms. This might involve challenges with reading, writing, math, or processing information, requiring additional support and accommodations.
Example: Alex demonstrates creativity in certain projects but struggles with reading and writing assignments, making it difficult for him to keep up with coursework.
Anxiety Disorder
The complexities of managing AuDHD symptoms can contribute to anxiety disorder, depression, and other mental health concerns. Seeking support from a qualified mental health professional is crucial for managing co-occurring conditions and promoting overall well-being.
Example: Sarah is going through the complexities of managing her AuDHD symptoms daily, creating a wide range of stressors. Over time, Sarah begins experiencing heightened anxiety and feelings of isolation.
Diagnosis and Support for the Symptoms of ADHD and ASD

Accurate diagnosis of AuDHD should be done by a qualified professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. They can assess the individual's specific symptoms and needs, recommend appropriate interventions, and connect them with supportive resources.
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) offers valuable resources and information on ADHD and co-occurring conditions like ASD. You may also obtain reliable information from other parents facing the same struggle through support groups and communities. Understanding the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial in children and teens with AuDHD.
Calming the brain so a neurodivergent child or teen can self regulate enough to learn coping strategies is critical.
The BrainBehaviorResetTM Program also provides help and support for families navigating AuDHD. The program incorporates science-backed solutions, such as neurofeedback, PEMF, and magnesium, to ensure that kids get the treatment and support they need without resulting in using medications that can affect their growth and behavior. By recognizing the complexities and seeking professional guidance, children and teens with AuDHD can navigate their challenges and thrive.
Parent Action Steps
☐ Listen to my podcast, It’s Gonna Be OK! ADHD podcast series and Autism episodes.
☐ Implement strategies for managing AuDHD symptoms
☐ Provide opportunities for social connections based on shared interests.
☐ Collaborate with mental health professionals for comprehensive support.
☐ Use the Solutions Matcher to get personalized science-backed solutions for your child.
Citations
Grzadzinski, R., Di Martino, A., Brady, E., Mairena, M. A., O’Neale, M., Petkova, E., Lord, C., & Castellanos, F. X. (2010). Examining Autistic Traits in Children with ADHD: Does the Autism Spectrum Extend to ADHD? Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 41(9), 1178–1191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-010-1135-3
Mayes, S. D., Calhoun, S. L., Mayes, R. D., & Molitoris, S. (2012). Autism and ADHD: Overlapping and discriminating symptoms. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 6(1), 277–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rasd.2011.05.009
Dr. Roseann is a mental health expert who frequently is in the media:
- Helping Children Thrive Podcast Benefits of Neurofeedback for children with ADHD
- Very Well Mind New Research Highlights Key Differences Among Autistic Boys and Girls
- She Knows 11 Products Moms of Kids With ADHD Swear By to Maintain Order in the Chaos
Very Well Mind What Is Asperger Syndrome?
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about science-backed solutions, so you are in the right place!
Grab your complimentary copy of
147 Therapist-Endorsed Self-Regulation Strategies for Children: A Practical Guide for Parents
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Licensed Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including The Mel Robbins Show, CBS, NBC, PIX11 NYC, Today, FORBES, CNN, The New York Times, The Washington Post, Business Insider, Women’s Day, Healthline, CNET, Parade Magazine and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She coined the terms, “Re-entry panic syndrome” and “eco-anxiety” and is a frequent contributor to media on mental health.
Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge has three decades of experience in working with children, teens and their families with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, concussion, dyslexia and learning disability, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), depression and mood disorder, Lyme Disease, and PANS/PANDAS using science-backed natural mental health solutions such as supplements, magnesium, nutrition, QEEG Brain maps, neurofeedback, PEMF, psychotherapy and other non-medication approaches.
She is the author of three bestselling books, It’s Gonna Be OK!: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child's Mental Health, The Teletherapy Toolkit, and Brain Under Attack. Dr. Roseann is known for offering a message of hope through science-endorsed methods that promote a calm brain.
Her trademarked BrainBehaviorResetⓇ Program and It’s Gonna be OK!Ⓡ Podcast has been a cornerstone for thousands of parents facing mental health, behavioral or neurodevelopmental challenges.
She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health, Neurotastic™Brain Formulas and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Mental Health Professional (CIMHP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2024