Parents often marvel at the incredible growth and development our children undergo. But do you really know what's happening inside those little minds and bodies? Understanding child development is like deciphering a secret code that unlocks the mysteries of your child's growth.
Child development encompasses various cognitive, social, emotional, and physical domains. It is a complex process that unfolds throughout different stages of a child's life. Understanding the principles of child development allows us to gain valuable insights into our children's unique journeys.
Many factors, such as genetics, learning environment, and experiences, affect child development. Knowing the stages and milestones of child development can help parents appreciate and support their children's growth.
Growing up, your child learns about metacognition and self-regulation. Metacognition refers to a person’s ability to think about and reflect upon one's thinking processes, while self-regulation involves managing one's emotions, behaviors, and attention. These related concepts are necessary for their own learning, mental health, and overall well-being.
If your child has an everyday problem with these skills, their story may resemble Ally's. Ally was a curious and determined young girl who loved learning and exploring new things. However, she often gets frustrated when things go differently than planned. She would get upset and give up easily whenever she faced challenges or made mistakes. She was a dysregulated kid who tended to have BIG reactions to small things.
Ally needed support in developing her metacognition and self-regulation skills for growth and success. These important skills are just one of the many areas Ally needs help with, and the role of her parents in this process was crucial in helping her eventually thrive.
Understanding Child Psychology
Children are not miniature adults. Their minds function differently, and their experiences shape their development uniquely. Child psychology explores how children perceive the world, process information, and interact with their environment.
A critical concept in child psychology is that children actively build their understanding of the world through their experiences and interactions. This concept is known as constructivism, which affects their development.
Children's relationships with their parents, caregivers, peers, and the broader social environment significantly impact their social and emotional development. They learn to regulate emotions, develop empathy, and navigate social interactions through them.
Child psychology can help us make sense of our children's behavior and emotions. It allows us to empathize with them, respond to their needs effectively, and provide appropriate support. It also sheds light on the individual differences among children.
Remember that every child is unique with their strengths, challenges, and temperament. We can tailor our parenting styles and teaching strategies by appreciating these differences to meet our child's needs.
What is Child Development?
Child development is a captivating and dynamic process encompassing children's physical, cognitive, social, and emotional growth from infancy through adolescence. It involves the intricate interplay between nature (genetics) and nurture (environment) that shapes children into the unique individuals they become.
Child development is a multifaceted journey marked by significant milestones and transformations. Parents need a solid understanding of this process to provide support and create a nurturing environment for their children's optimal growth.
At its core, child development encompasses the changes and advancements in children's bodies, minds, and abilities as they gain additional progress through different stages of life. It involves physical aspects, such as height, weight, motor skills, cognitive processes, executive functions, language acquisition, social interactions, and emotional regulation.
Children are innately curious and naturally want to explore the world around them. From the day they are born, they embark on a remarkable journey of discovery. They are constantly absorbing information and learning from their environment.
Child development can be broadly categorized into several domains. Let's explore each of them to gain a deeper understanding of the intricacies of child development:
Child Development Domains: Understanding How Kids' Brains and Bodies Develop
Physical Development
Physical development pertains to the changes in a child's body and physical abilities. It includes gross motor skills, such as crawling, walking, and running, and fine motor skills, such as grasping objects, using utensils, and writing. Physical development also encompasses body proportions, muscle strength, and coordination changes.
Cognitive Development
Cognitive development involves the growth of a child's thinking, problem-solving, and intellectual abilities. It includes the development of language skills, memory, attention, reasoning, and creativity. As children develop cognitive function, they learn complex reasoning and abstract logic. Thinking skills are important in everyday life and there are many things we can do to enhance cognitive functioning.
Social Development
Social development focuses on how children interact with others and navigate social relationships. It includes developing social skills, empathy, cooperation, and understanding of social norms. In addition, children learn to communicate, form friendships, and create a sense of identity within their social environment.
Emotional Development
Emotional development involves the children's ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions. It includes the development of self-awareness, empathy, emotional regulation, and coping skills. Children start to identify and express their emotions, understand the feelings of others, and navigate the complexities of their emotional world.
Child Development Stages and How They Relate to Metacognition and Self-Regulation Skills
Early childhood development is a critical period that builds the foundation for a child's future success and well-being. During these formative years, children undergo rapid growth and development. They acquire essential skills and capabilities that shape their overall trajectory in life. These years form the basis of just how the nervous system learns to self regulate.
How we parent has a huge impact on child development. When we are regulated, our children are more regulated. If we bring our own toxic parenting history to the table, our kids will often display those same behaviors that repel us.
The early years are characterized by significant brain development and neural connections from birth to age six. Recent research shows that the brain undergoes a period of intense plasticity during this time. At this stage, the brain is highly receptive to learning and experiences (Ismail et al., 2017). They literally soak everything in. Children's brain development forms the foundation for cognitive, social, emotional, and physical development during this crucial period.
Child development stages are crucial in shaping a child's metacognition and self-regulation skills. Parents should learn how these cognitive processes evolve throughout different stages of child development. It will give them valuable insights into fostering their growth and providing support. Soon, their children will become self-aware and self-regulated individuals.
Infancy
In the infancy stage, metacognition and self-regulation are in their earliest stages of development. Babies begin to develop an awareness of their bodies. They also start to regulate their basic physiological needs, such as hunger and sleep.
They learn to recognize familiar caregivers and respond to their presence. While metacognitive abilities are still developing, infants use primary forms of self-regulation. They communicate their needs through crying and physical cues.
Early Childhood
As children enter early childhood, metacognitive awareness begins to emerge. They develop a greater understanding of themselves as individuals with distinct thoughts, feelings, and desires. They become aware of their preferences and express their likes and dislikes.
Self-regulatory skills also progress during this stage. Children learn to control their impulses, follow simple rules, and engage in cooperative play with others. In addition, they develop a basic sense of right and wrong and regulate their behavior to align with social expectations.
Middle Childhood
In middle childhood, their metacognition and self-regulation approaches become more advanced. Children can reflect on their thinking processes and apply strategies to solve problems. They recognize their strengths and weaknesses and develop strategies to enhance their learning.
In this age group, self-regulation becomes more intentional. Children can set goals, manage time, and regulate emotions more effectively. In addition, they engage in self-monitoring and begin to understand the consequences of their actions.
Adolescence
During adolescence, metacognition and self-regulation skills reach a higher level of complexity. Teenagers develop metacognitive abilities such as planning, setting goals, and monitoring their progress. They become more aware of their cognitive processes and can adjust their strategies accordingly.
Self-regulation skills continue to mature as teenagers learn to manage their emotions, navigate social interactions, and make responsible decisions. They also develop a sense of identity and values, influencing self-regulatory abilities.
Importance and Effectiveness of Metacognition and Self-Regulation Skills in Child Development
Kids need to be self-regulated to learn. Without self-regulation, children and teens can display a host of problems. Good metacognition is an important part of learning to do just that.
Metacognition is awareness of our thoughts, while self-regulation controls our actions and emotions. Both are important to learn when growing up. These skills help us do well in school, feel good about ourselves, and keep learning.
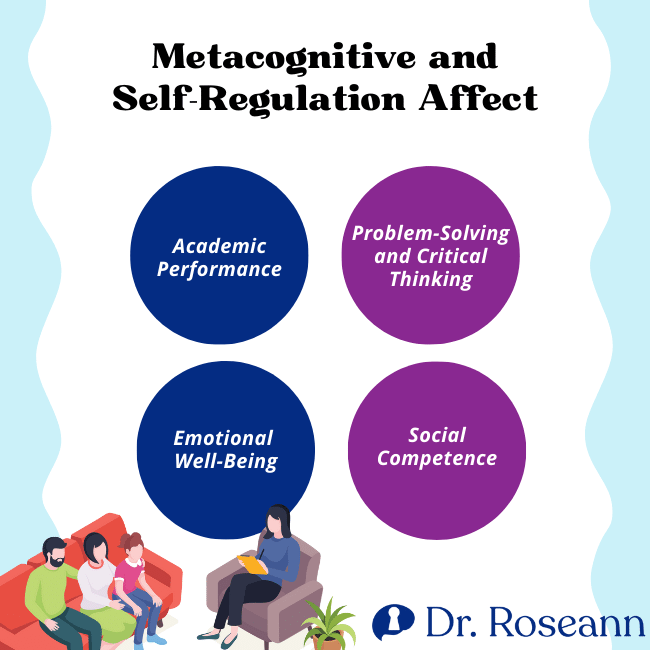
These brain processes are super important because they help us know ourselves better, become smarter, and handle challenging situations. Here are some specific ways metacognition and self-regulation help us the most:
Academic Performance: Metacognition and Self Regulated Learning
Metacognition and self-regulation skills are essential for academic success. These skills help kids keep track of how they learn, set goals, and use good strategies to learn different things. Kids can change their study habits When they understand how they learn best.
They are also more confident when asking for help and keep going even when things are hard. Self-regulation skills, like managing time, staying focused, and controlling impulses, help them complete their academic tasks.
They also become active learners and can make changes to learn better. Self-regulation skills help kids ignore distractions, decide what's important, and concentrate on it. With these skills, kids can take charge of their learning and keep learning outside the school's curriculum.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Metacognition is crucial for developing problem-solving and critical thinking skills. It helps us look at problems closely, devise solutions, and determine the most effective strategies. With this ability, we become more flexible in our thinking. We can handle new situations and approach challenges with a positive attitude.
Conversely, self-regulation is about controlling our impulses, thinking about different viewpoints, and understanding the consequences of our actions. These skills help us make good decisions. Combining metacognition and self-regulation makes us even better at solving problems. It prepares us to face all sorts of difficult situations in different areas of life.
Emotional Well-Being
Metacognition and self-regulation are connected to how we feel inside. When we understand and manage our emotions well, it helps us feel better. We can learn ways to handle stress, anxiety, and frustration by recognizing and thinking about our feelings.
It also helps us understand what makes us feel certain ways and how our feelings can affect our thoughts and actions. We can learn positive ways to deal with our emotions. We must control our feelings, express them well, and keep a positive balance. As we do this, we become strong when things get tough. Handling conflicts and maintaining good relationships with others becomes a walk in the park.
Social Competence
Metacognitive skills help us think about how our actions can affect others. That way, we can change our actions and become more considerate. Self-regulation skills help us control our impulses, manage our emotions, and communicate effectively. This way, we can have good relationships with others and treat them positively.
Understanding what others might think, feel, and want makes us more caring and understanding toward them. We become better at being kind, solving conflicts, and understanding how others feel. It will also help us have healthy relationships and get along well with others.
Strategies for Developing Metacognition and Self-Regulatory Skills in Children
Parents can employ several effective metacognition and self-regulation strategies to foster the growth of these crucial skills. However, developing these skills in children is a gradual process that requires consistent support and guidance.
1. Promote Reflection and Self-Awareness
Encourage your child to reflect on their learning experiences by asking open-ended questions. Prompt them to think about what strategies worked, what challenges they faced, and how they can improve in the future. Help them know their strengths and areas for growth to foster a sense of self-awareness and mood control.
2. Teach Goal Setting
Work with your child to set specific, achievable goals. Break down big goals into smaller tasks to make progress more tangible. Regularly review and revise goals with your child, celebrating achievements and adjusting as necessary. This process helps children understand the importance of setting targets and tracking their progress.
3. Model Metacognitive Thinking
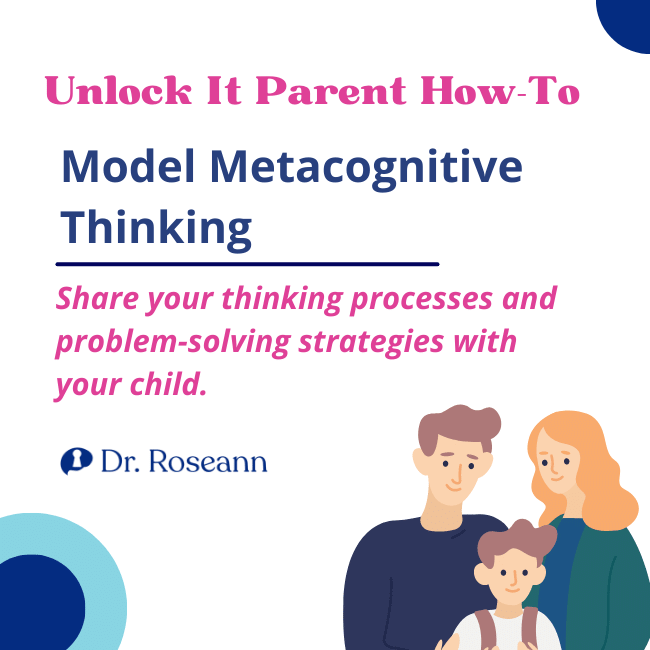
Share your thinking processes and problem-solving strategies with your child. Narrate your thoughts aloud when faced with challenges or decision-making situations. Explicit teaching and demonstrating the value of reflection and thoughtful decision-making would help.
4. Encourage Metacognitive Strategies
Teach your child different metacognitive strategies that can enhance their learning process. These may include techniques such as self-questioning. For example, you may encourage them to ask, “What strategy can I use to solve this problem?”
Summarizing information, visualizing concepts, or connecting to prior knowledge will help them too. Encourage your kids to use these strategies independently and reflect on their effectiveness.
5. Foster a Growth Mindset
Emphasize the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through effort and practice. Inspire your child to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than obstacles. Nix the negativity bias and teach your child to focus on the positive. Praise their efforts, persistence, and strategies rather than solely focusing on outcomes. This mindset promotes resilience and a willingness to take on new challenges.
6. Establish Routines and Structure
Help your child establish consistent routines for studying, completing homework, and engaging in other activities. A consistent structure provides a framework for self-regulation and helps children develop discipline and time management skills. Provide a quiet, organized workspace that minimizes distractions and promotes focus.
7. Teach Emotional Regulation
Help your child manage and understand their emotions by teaching them strategies for emotional regulation. Encourage them to identify their emotions, express them appropriately, and explore healthy coping mechanisms. Practice deep breathing exercises, mindfulness techniques, or journaling, a powerful tool for emotional self-regulation.
8. Encourage Reflection on Mistakes
Show your child that mistakes can be great opportunities for learning and growth. Encourage them to analyze their mistakes and identify areas for learning and improvement. Help them understand that making mistakes is a natural part of learning and that seeking assistance or trying different strategies is okay.
9. Provide Opportunities for Independent Learning
Foster independent thinking and decision-making by allowing your child to make choices and solve problems. Groom them to become independent learners, but offer guidance and support. Give them space to explore their solutions and learn from their experiences. Encouraging independence nurtures self-regulation and metacognitive skills.
10. Collaborate with Educators
Maintain open lines of communication with your child's classroom teacher throughout the school year to gain insights into their academic activities and expectations. Share strategies that have worked well at home and inquire about classroom practices supporting metacognition and self-regulation. Collaboration with educators enhances consistency and reinforces the development of these skills. Some kids may require an IEP or 504 plan to become self-regulated students.
Parent’s Role in Developing Metacognition and Self-Regulatory Skills in Kids
Children need their parent's support in developing metacognition and self-regulation skills. You can empower your children to become self-aware, resilient, and successful learners through support, modeling, communication, and emotional regulation.
Returning to Ally's story, her parents addressed the problem by creating a nurturing and supportive environment at home. Once they calmed her nervous system with supplements, good nutrition and magnesium, they focused on skill building. They encouraged Ally to express her thoughts and emotions openly while they listened attentively to her ideas and concerns.
I advised her parents to start modeling metacognitive and self-regulatory behaviors to support Ally further. We shared stories of challenges and how to overcome them through reflection and thoughtful decision-making. Soon enough, Ally saw how her parents take breaks to think and plan before handling complicated tasks, which inspired her to do the same.
Over time, Ally's metacognition and self-regulation skills blossomed. She became more aware of her learning processes and developed strategies to tackle complex issues. Ally embraced challenges with a growth mindset and viewed them as opportunities to learn and grow. Her ability to reflect, set goals, regulate her emotions, and stay focused allowed her to navigate various situations confidently.
Unlock the secrets to successful self-regulation for your child! Our free resource, “147 Therapist-Endorsed Self-Regulation Strategies for Children: A Practical Guide for Parents,” is a game-changer. Access your copy now and discover practical strategies endorsed by therapists. Don't miss out, download here: www.drroseann.com/self-regulation-strategies
Citation
Hayat AA, Shateri K, Amini M, Shokrpour N. Relationships between academic self-efficacy, learning-related emotions, and metacognitive learning strategies with academic performance in medical students: a structural equation model. BMC Med Educ. 2020 Mar 17;20(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-01995-9. PMID: 32183804; 10.1186/s12909-020-01995-9
Ismail, F. Y., Fatemi, A., & Johnston, M. V. (2017). Cerebral plasticity: Windows of opportunity in the developing brain. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology, 21(1), 23–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2016.07.007
Sahranavard S, Miri MR, Salehiniya H. The relationship between self-regulation and educational performance in students. J Educ Health Promot. 2018 Dec 28;7:154. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_93_18. PMID: 30693291; 10.4103/jehp.jehp_93_18
Always remember… “Calm Brain, Happy Family™”
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about solutions, so you are in the right place!
There are 3 ways to work with Dr. Roseann:
You can get her books for parents and professionals, including: It’s Gonna Be OK™: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child’s Mental Health, Teletherapy Toolkit™ and Brain Under Attack: A Resource For Parents and Caregivers of Children With PANS, PANDAS, and Autoimmune Encephalopathy.
If you are a business or organization that needs proactive guidance to support employee mental health or an organization looking for a brand representative, check out Dr. Roseann’s media page and professional speaking page to see how we can work together.
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Licensed Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including The Mel Robbins Show, CBS, NBC, PIX11 NYC, Today, FORBES, CNN, The New York Times, The Washington Post, Business Insider, Women’s Day, Healthline, CNET, Parade Magazine and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She coined the terms, “Re-entry panic syndrome” and “eco-anxiety” and is a frequent contributor to media on mental health.
Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge has three decades of experience in working with children, teens and their families with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, concussion, dyslexia and learning disability, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), depression and mood disorder, Lyme Disease, and PANS/PANDAS using science-backed natural mental health solutions such as supplements, magnesium, nutrition, QEEG Brain maps, neurofeedback, PEMF, psychotherapy and other non-medication approaches.
She is the author of three bestselling books, It’s Gonna Be OK!: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child's Mental Health, The Teletherapy Toolkit, and Brain Under Attack. Dr. Roseann is known for offering a message of hope through science-endorsed methods that promote a calm brain.
Her trademarked BrainBehaviorResetⓇ Program and It’s Gonna be OK!Ⓡ Podcast has been a cornerstone for thousands of parents facing mental health, behavioral or neurodevelopmental challenges.
She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health, Neurotastic™Brain Formulas and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Mental Health Professional (CIMHP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2023
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to give health advice and it is recommended to consult with a physician before beginning any new wellness regime. *The effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment vary by patient and condition. Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC does not guarantee certain results.