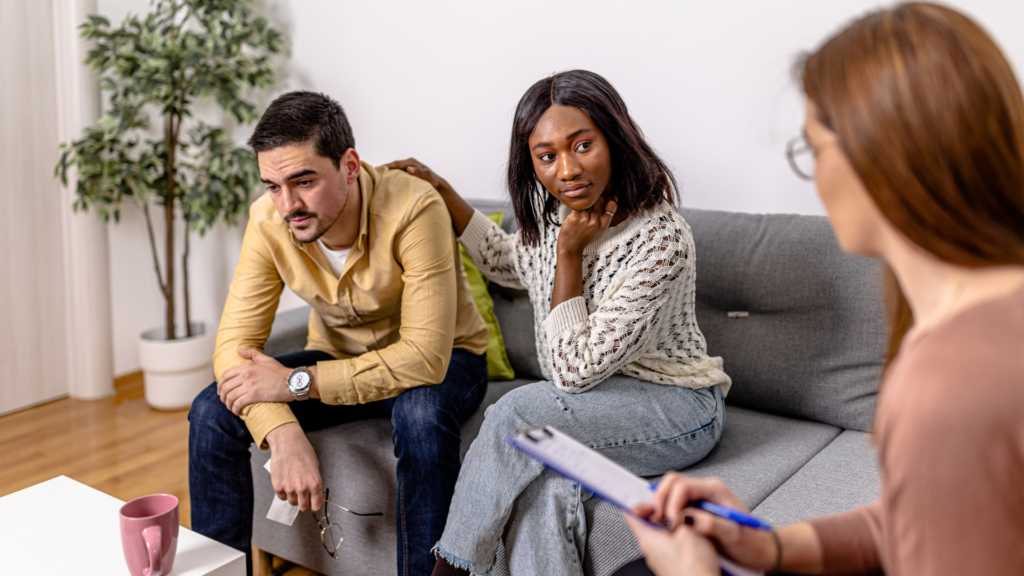
Raising a child who consistently resists and avoids demands can be bewildering and emotionally draining. While their tantrums and meltdowns might appear defiant, a different explanation may lie beneath the surface – Pathological Demand Avoidance (PDA).
Parents must understand what it means to have a PDA diagnosis and what they can do to help their child manage the symptoms.
PDA Traits and Symptoms
PDA was coined by Professor Elizabeth Newson in the 1980s (Woods, 2019). However, this condition has yet to be a formal diagnosis in manuals like the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) or the International Statistical Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). PDA emerges as a distinct profile within the Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) umbrella, making it quite common among autistic children.
Pathological Demand Avoidance is intricately linked to an autism diagnosis or pervasive developmental disorder, being a distinct profile within the spectrum. Sharing commonalities with autistic people, individuals with PDA exhibit social and communication challenges, heightened sensory sensitivities, defiance of authority figures, and emotional difficulties, among others,
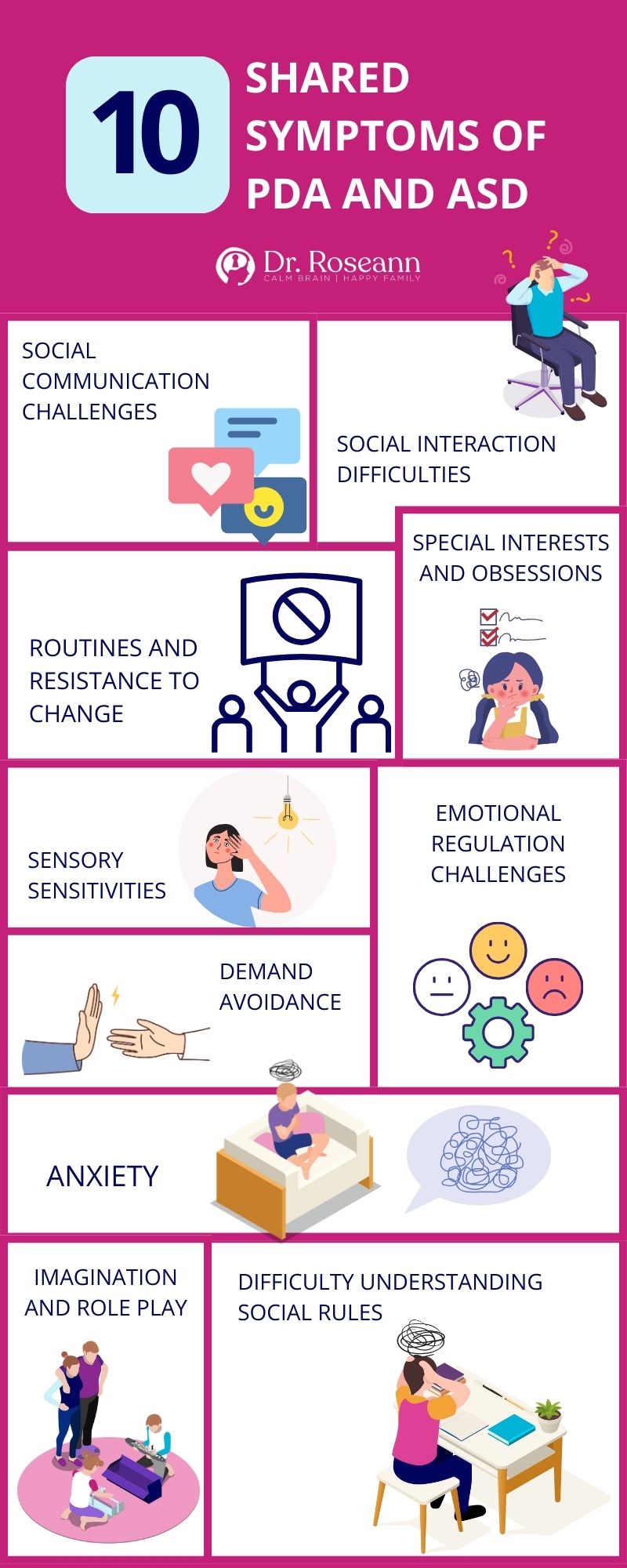
However, what sets PDA apart is the intense and pervasive avoidance behavior. These kids may react severely to everyday demands, driven by a deep-seated need for control and fear of losing autonomy.
This demand avoidance, coupled with unique social strategies and emotional volatility, contributes to the distinct presentation of PDA.
Here is a detailed explanation of the symptoms of PDA.
- Intense Demand Avoidance: People with PDA go to an extreme extent to achieve avoidance of everyday demands, from brushing their teeth to schoolwork. Their need is driven by a deep-seated need for control and fear of losing autonomy.
- Use of Social Strategies: To avoid demands, they may employ tactics like distraction, negotiation, questioning, or even meltdowns that often appear as manipulative or willful.
- Emotional Volatility: High anxiety and frustration fuel their resistance, leading to unpredictable emotional outbursts or a potential panic attack.
- Sensory Processing Issues: Many children with the PDA profile of autism have heightened sensory sensitivities, making certain demands, like haircuts or noisy environments, particularly overwhelming.
Diagnosing PDA
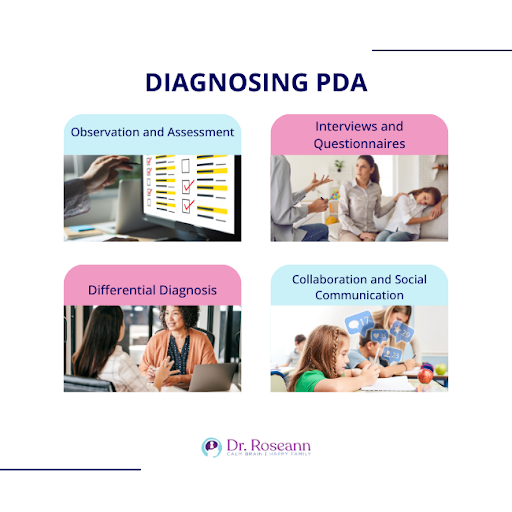
Due to its evolving nature, diagnosing PDA requires a meticulous approach. Here are the steps performed by qualified mental health professionals to diagnose PDA in kids, older children, teens, and adults, which also serve as a diagnostic tool for healthcare professionals specialized in pathological demand avoidance syndrome and autism assessments.
1. Observation and Assessment
Clinicians will closely observe the child’s social interaction and behavior in various settings, including home, school, and social situations. They'll pay particular attention to the intensity and frequency of demand avoidance, social strategies used to negotiate or escape demands, emotional responses, and sensory processing patterns.
2. Interviews and Questionnaires
In-depth interviews are conducted with the individual and their caregivers, parents, and teachers to gather detailed information about their experiences, challenges, and coping mechanisms. Standardized questionnaires like the Extreme Demand Avoidance Questionnaire (EDA-Q) can be used to assess the core features of PDA (O’Nions et al., 2013), although it's important to remember that these are not diagnostic tools in themselves.
3. Differential Diagnosis
A crucial aspect of the assessment is to rule out other potential explanations for the observed PDA behaviors. This might involve considering conditions like anxiety, oppositional defiant disorder, and ADHD.
4. Collaboration and Social Communication
A team approach is often necessary, involving specialists like developmental pediatricians, clinical psychologists, occupational therapists, and speech-language pathologists.
Clear communication and collaboration between all parties involved are essential for ensuring a comprehensive and accurate assessment.
However, there's no single test or definitive marker for PDA. The diagnosis is based on a careful analysis of the child’s unique presentation and symptoms. While PDA shares some characteristics with ASD, it also has distinct features and may not always neatly fit into the traditional diagnostic criteria for ASD. Receiving a PDA diagnosis can help access appropriate support and interventions tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Support for Parents
Living with a child with PDA can be a very emotional journey, but knowing what to expect and where to turn for help can make a world of difference. Getting support from a local PDA society, support group or community can give parents access to comprehensive resources and guidance.
Understanding and recognizing the underlying fear and anxiety driving your child's behavior can help you approach them with empathy and patience. To help with that, strive to develop clear and consistent communication strategies that respect your child's need for control while setting necessary boundaries.
There are also a lot of alternative approaches available for your kids. Explore positive reinforcement, role play and pretending, and sensory tools to navigate potentially challenging situations.
The BrainBehaviorResetTM Program uses natural solutions to address neurological imbalances and their underlying behavioral and emotional challenges in children and teens. It involves identifying root causes through assessments of brain function, sensory processing, and emotional regulation. Targeted interventions, such as neurofeedback and sensory integration therapy, aim to address imbalances.
Seeking professional help for yourself and your child can equip you with coping mechanisms and ensure everyone's well-being. By collaborating with professionals, you build knowledge and prioritize your mental health. You can ensure your child receives the support they need to thrive in a world that often feels full of demands.
Parent Action Steps
☐ Learn about PDA symptoms and traits from a qualified healthcare provider to better understand your child's challenges.
☐ Keep a record of your child's behaviors, noting instances of demand avoidance and emotional responses.
☐ Foster open dialogue with family members, teachers, caregivers, and professionals to gather diverse perspectives.
☐ Join local PDA support groups for shared experiences on social challenges and comprehensive resources on the key features of PDA.
☐ Take the Solutions Matcher to get personalized treatment for your child and improve their pattern of behavior.
Citations
O’Nions, E., Christie, P., Gould, J., Viding, E., & Happé, F. (2013). Development of the “Extreme Demand Avoidance Questionnaire” (EDA-Q): preliminary observations on a trait measure for Pathological Demand Avoidance. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 55(7), 758–768. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12149
Woods, R. (2019). Demand avoidance phenomena: circularity, integrity and validity – a commentary on the 2018 National Autistic Society PDA Conference. Good Autism Practice, 20(2), 28–40. https://openresearch.lsbu.ac.uk/item/8qx90
Dr. Roseann is a mental health expert who frequently is in the media:
- Helping Children Thrive Podcast Benefits of Neurofeedback for children with ADHD
- Very Well Mind New Research Highlights Key Differences Among Autistic Boys and Girls
- She Knows 11 Products Moms of Kids With ADHD Swear By to Maintain Order in the Chaos
Very Well Mind What Is Asperger Syndrome?
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about science-backed solutions, so you are in the right place!
Grab your complimentary copy of
147 Therapist-Endorsed Self-Regulation Strategies for Children: A Practical Guide for Parents
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Licensed Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including The Mel Robbins Show, CBS, NBC, PIX11 NYC, Today, FORBES, CNN, The New York Times, The Washington Post, Business Insider, Women’s Day, Healthline, CNET, Parade Magazine and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She coined the terms, “Re-entry panic syndrome” and “eco-anxiety” and is a frequent contributor to media on mental health.
Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge has three decades of experience in working with children, teens and their families with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, concussion, dyslexia and learning disability, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), depression and mood disorder, Lyme Disease, and PANS/PANDAS using science-backed natural mental health solutions such as supplements, magnesium, nutrition, QEEG Brain maps, neurofeedback, PEMF, psychotherapy and other non-medication approaches.
She is the author of three bestselling books, It’s Gonna Be OK!: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child's Mental Health, The Teletherapy Toolkit, and Brain Under Attack. Dr. Roseann is known for offering a message of hope through science-endorsed methods that promote a calm brain.
Her trademarked BrainBehaviorResetⓇ Program and It’s Gonna be OK!Ⓡ Podcast has been a cornerstone for thousands of parents facing mental health, behavioral or neurodevelopmental challenges.
She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health, Neurotastic™Brain Formulas and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Mental Health Professional (CIMHP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2024










