When we think of neurodivergence, we think of a list of clinical conditions that might interfere with learning, attention and social functioning. On the flip side, these conditions come with many strengths too.
What is Neurodivergence?
Neurodiversity covers a spectrum of neurological differences, including but not limited to autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and more. But rather than viewing these variances as deficits, neurodiversity celebrates these differences as unique strengths that contribute to the rich human experience.
Neurodivergent traits refer to a wide array of cognitive styles, communication patterns, and ways of processing information. Neurodiverse individuals often exhibit exceptional talents in areas such as pattern recognition, problem-solving, creativity, and attention to detail. While these traits may manifest differently from person to person, they collectively represent the diverse spectrum of human cognition.

Facts About Neurodiversity: Debunking Misconceptions
One common misconception about neurodiversity is that it is synonymous with impairment or disability. However, this overlooks the countless strengths and advantages that these exceptional individuals bring to the table. Contrary to popular belief, neurodiversity is not a hindrance but rather a source of innovation, resilience, and unique perspectives.
Neurodivergent individuals often exhibit exceptional problem-solving skills, creativity, and attention to detail. Their ability to think outside the box can lead to groundbreaking discoveries and solutions in various fields, including science, technology, engineering, and the arts (Asbell-Clarke, 2023). Additionally, a neurodivergent person may have a heightened sensitivity to patterns, allowing them to excel in fields such as mathematics, computer programming, and music composition.
Moreover, neurodiversity fosters a culture of inclusivity and acceptance, where individuals are valued for their differences rather than stigmatized for their challenges. Organizations embracing neurodiversity can create environments that encourage collaboration, innovation, and mutual respect.
To achieve all these, parents should start by supporting their children and aid in providing school accommodations tailored to their needs. Their school can help unlock their full potential, which starts by debunking misconceptions and embracing neurodiversity. Once society learns to harness neurodiversity, we can create a more inclusive and equitable world for all.
Neurodiversity Strengths Checklist
Are you curious, detail-oriented, or exceptionally creative? These may be indicators of neurodivergent strengths. Take a moment to reflect on your cognitive traits and consider how they contribute to your personal and professional endeavors. Embracing neurodiversity means embracing the diverse range of talents and abilities that each individual possesses.
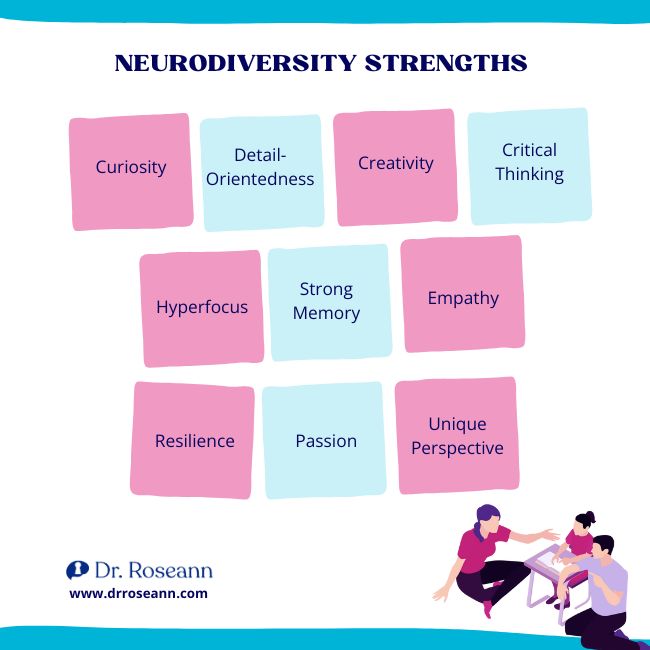
Neurodiversity Strengths
1. Curiosity
Embracing curiosity means you possess a natural inclination to explore and seek out new information. This trait fuels a lifelong pursuit of knowledge and understanding, driving innovation and discovery.
2. Detail-Orientedness
Being detail-oriented allows you to notice patterns, discrepancies, and nuances that others might overlook. This attention to detail enhances accuracy and precision in tasks, contributing to high-quality work and problem-solving.
3. Creativity
Exceptional creativity enables you to think outside the box, envisioning new possibilities and solutions. This imaginative capacity fosters innovation and originality in artistic expression, problem-solving, and conceptual thinking.
4. Critical Thinking
Excelling at critical thinking means you can analyze complex information, evaluate evidence, and draw logical conclusions. This skill enhances decision-making and problem-solving abilities, leading to effective solutions and informed choices.
5. Hyperfocus
Hyperfocus allows you to fully immerse yourself in tasks or activities that capture your interest. This intense concentration can result in heightened productivity and deep engagement with projects, leading to exceptional outcomes.
6. Strong Memory
A strong memory for specific details, facts, or information enables you to recall information accurately and efficiently. This trait facilitates learning, information retention, and effective communication, enhancing overall cognitive abilities.
7. Empathy
Possessing empathy means you are attuned to the emotions and experiences of others, fostering meaningful connections and understanding. This trait promotes cooperation, collaboration, and supportive relationships in personal and professional settings.
8. Resilience
Demonstrating resilience in the face of challenges or setbacks means you can adapt and bounce back from adversity. This ability to overcome obstacles strengthens perseverance, determination, and personal growth.
9. Passion
Intense interests or passions drive your pursuits and motivate you to delve deeply into certain subjects or activities. This enthusiasm fuels dedication, commitment, and achievement, leading to fulfillment and academic success.
10. Unique Perspective
Offering a unique perspective or approach to problem-solving means you can see things from a different angle than others. This diversity of thought fosters creativity, innovation, and inclusive decision-making, enriching collaborative efforts and outcomes.
Neurodivergent Thinking and Unlocking Creative Potential
Neurodivergent thinking is characterized by its nonlinear, out-of-the-box approach to problem-solving and decision-making. Unlike neurotypical thinking, which tends to follow conventional patterns, neurodivergent thinking thrives on unconventional connections, novel ideas, and innovative solutions.
But while neurodiversity brings with it a host of strengths and advantages, it is not without its challenges. Neurodivergent individuals may encounter obstacles that require understanding and support from their peers and communities, particularly when navigating social interactions and managing sensory sensitivities.
In an increasingly complex and rapidly changing world, diversity of thought has never been more crucial. Embracing neurodiversity means tapping into a wealth of untapped talent and potential. Studies have shown that diverse teams are more innovative, adaptable, and resilient, making neurodiversity not only a moral imperative but also a strategic advantage (Wang et al., 2019).
Ultimately, embracing neurodiversity is not just about recognizing individual differences. It's about building a more inclusive and equitable society for all. Neurodiversity is not a limitation but rather a source of strength, innovation, and resilience.
Finding Neurodivergence Strength Next Steps
Learning how the neurodivergent brain works and gaining strategies to foster neurodivergent strengths is your next step. Taking our course, Self-Regulation Mastery: A Parent's Path to Understanding and Managing Children's Dysregulated Behaviors and Emotions, is your next step. It gives you actionable tools to start helping your child today!
What are neurodivergent traits?
Neurodivergent traits encompass a wide range of cognitive, sensory, and behavioral characteristics found in a neurodiverse person, such as heightened sensitivity, unique communication styles, and diverse learning approaches. Neurodiverse examples include autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and Tourette syndrome.
Am I neurodiverse?
Whether you're neurodiverse or neurodivergent gifted, recognizing and leveraging your neurodivergent traits can lead to personal growth and success. Start to embrace the benefits of neurodiversity such as enhanced problem-solving skills, creativity, and unique perspectives.
What percent of the population is neurodivergent?
Estimates suggest that up to 20% of the population are neurodivergent individuals. Their neurodivergent brain exhibits a spectrum of cognitive, sensory, and behavioral neurodivergent characteristics across different contexts and environments.
What are examples of being neurodivergent?
Facts about neurodiversity encompass a broad range of neurodivergent conditions, including autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, dyspraxia, and Tourette syndrome, among others. Each of these neurodivergent examples represents a unique manifestation of unique traits that highlights the diversity and complexity within the community.
What makes you neurodivergent?
Being neurodivergent entails having diverse strengths and cognitive traits that deviate from the neurotypical norm. These strengths can include heightened creativity, exceptional attention to detail, and unique problem-solving abilities, contributing to the richness and diversity of human cognition.
What are neurodivergent people good at?
A neurodiverse person often excels in areas that require unconventional thinking, such as problem-solving, pattern recognition, and innovation. Embracing neurodiversity facts acknowledges the valuable contributions neurodivergent people make to society through their exceptional talents and abilities.
How to know you are neurodivergent?
Recognizing neurodivergence involves identifying with traits commonly associated with neurodiversities, such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, or others. Checking a neurodivergence list can help individuals understand and recognize patterns in their behavior, cognition, and sensory experiences that align with neurodiverse traits.
Is everyone neurodivergent?
While everyone may exhibit some neurodivergent traits, not everyone meets the criteria for specific types of neurodivergence, such as autism, ADHD, or dyslexia. Neurodiversity statistics suggest that up to 20%of the population may have neurodivergent traits, but this does not mean that everyone is neurodivergent in the clinical sense.
Is neurodivergence real?
Neurodivergence is real, as it reflects the natural variation in the neurodiversity brain’s structure and function among individuals. Neurodivergencies list various diagnostic criteria observed in clinical settings, which further validate the reality of neurodiversity and the unique challenges and strengths associated with neurodivergent adults.
What makes someone neurodivergent?
Someone is considered neurodivergent when they exhibit neurodivergencies, which are variations in their neurodiverse brain structure and function that diverge from the typical neurotypical profile. Neurodiverse examples include conditions such as autism spectrum disorder, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, and Tourette syndrome, among others.
Are neurodivergents smarter?
The intelligence of neurodivergent individuals varies widely and cannot be generalized. While some may demonstrate exceptional abilities in specific areas due to their divergent brain function, others may face neurodiverse challenges that impact traditional measures of intelligence. Neurodivergent types encompass a spectrum of cognitive profiles, each with its strengths and weaknesses,
Citations
Asbell-Clarke, J. (2023). Reaching and Teaching Neurodivergent Learners in STEM. Taylor & Francis.
Wang, J., Cheng, G. H. ‐L., Chen, T., & Leung, K. (2019). Team creativity/innovation in culturally diverse teams: A meta‐analysis. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 40(6), 693–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2362
Dr. Roseann is a mental health expert in Neurodivergence who frequently is in the media:
- Think Inclusive How Families Can Support Twice Exceptional Children
- Insights to Live By (Podcast) Parenting for Mental Wellness
- Light from the Rabbit Hole Podcast Destigmatizing Mental Health
Always remember… “Calm Brain, Happy Family™”
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to give health advice and it is recommended to consult with a physician before beginning any new wellness regime. *The effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment vary by patient and condition. Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC does not guarantee certain results.
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about science-backed solutions, so you are in the right place!
Grab your complimentary copy of
147 Therapist-Endorsed Self-Regulation Strategies for Children: A Practical Guide for Parents
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Licensed Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including The Mel Robbins Show, CBS, NBC, PIX11 NYC, Today, FORBES, CNN, The New York Times, The Washington Post, Business Insider, Women’s Day, Healthline, CNET, Parade Magazine and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She coined the terms, “Re-entry panic syndrome” and “eco-anxiety” and is a frequent contributor to media on mental health.
Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge has three decades of experience in working with children, teens and their families with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, concussion, dyslexia and learning disability, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), depression and mood disorder, Lyme Disease, and PANS/PANDAS using science-backed natural mental health solutions such as supplements, magnesium, nutrition, QEEG Brain maps, neurofeedback, PEMF, psychotherapy and other non-medication approaches.
She is the author of three bestselling books, It’s Gonna Be OK!: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child's Mental Health, The Teletherapy Toolkit, and Brain Under Attack. Dr. Roseann is known for offering a message of hope through science-endorsed methods that promote a calm brain.
Her trademarked BrainBehaviorResetⓇ Program and It’s Gonna be OK!Ⓡ Podcast has been a cornerstone for thousands of parents facing mental health, behavioral or neurodevelopmental challenges.
She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health, Neurotastic™Brain Formulas and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Mental Health Professional (CIMHP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2024










