Depression and mood disorders are common in children and adults. In this pandemic world, I have seen an uptick in mood and anxiety-related conditions due to lingering effects of social isolation in my Ridgefield, CT clinic.
Moreover, there is also a rise in neurodivergence. Many parents are asking if depression is neurodivergent. It’s time to debunk myths and provide clarity on this complex issue.
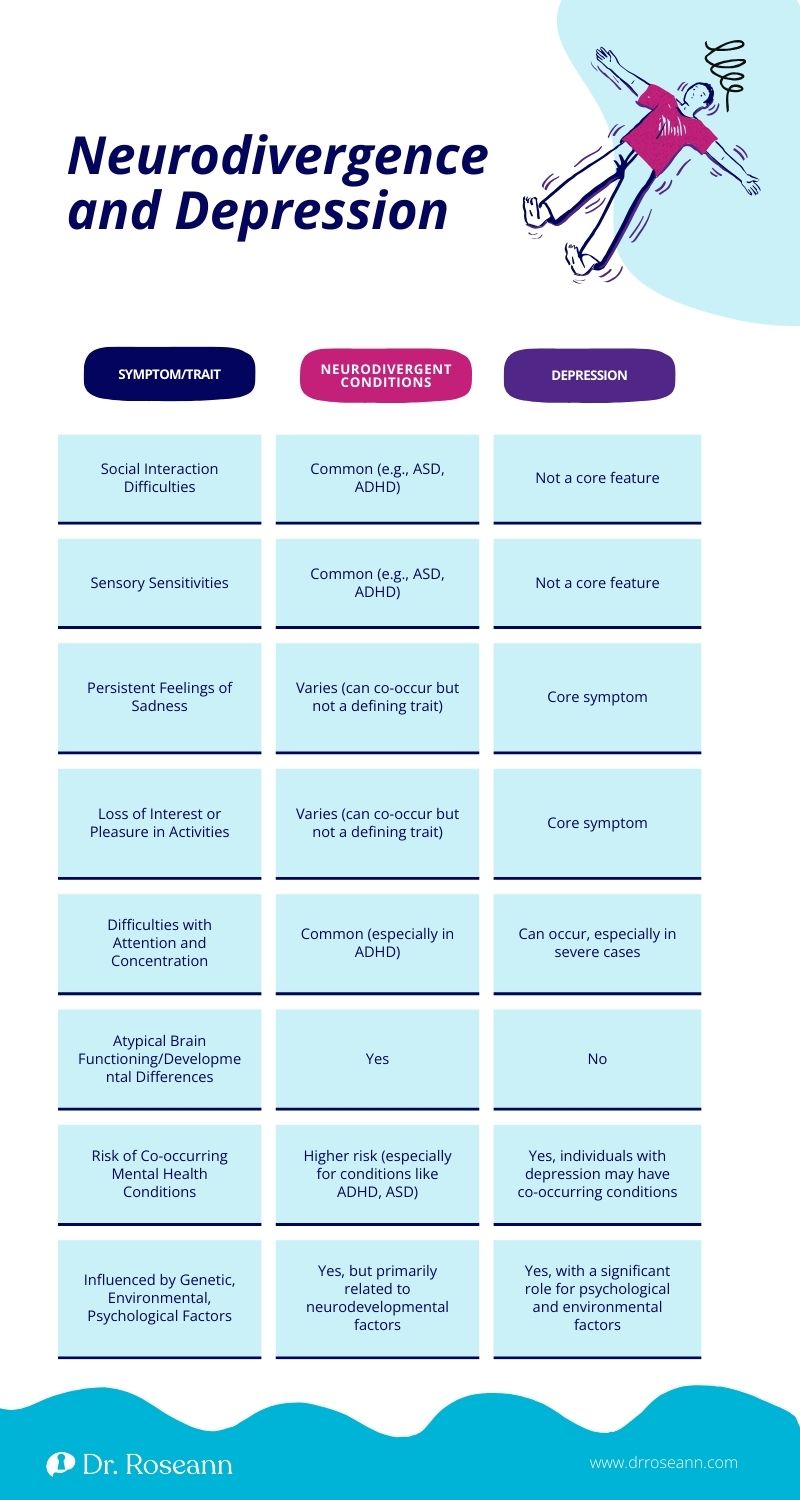
Neurodivergence refers to variations in the human brain regarding sociability, learning, attention, mood, and other mental functions. Neurodivergence refers to a spectrum of variations in cognitive, emotional, and behavioral traits. And those with neurodivergence may or may not have mood issues as well.
Neurodivergents may experience differences in processing information, social interaction, communication, and sensory perception. This neurodivergent umbrella term includes conditions such as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), dyslexia, dyspraxia, and more.
Understanding Depression
Depression, is also referred to as a mood disorder, involves persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a loss of interest or pleasure in activities. What I see in children and adults, is that it affects how individuals think, feel, and handle daily activities significantly impacting one's quality of life.
Depression can manifest in various forms, including major depressive disorder, persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia), seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and bipolar disorder. It also can affect individuals of all ages, although I don't see it commonly in very young children without some kind of traumatic experience.
So, is depression neurodivergent? The straightforward answer is no, depression itself is not classified as a neurodivergent condition. Depression can occur at any stage of life and is often influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. Neurodivergent conditions, on the other hand, typically involve atypical brain functioning and developmental differences (Mirowsky & Ross, 1992).
Does Depression Make You Neurodivergent?
While depression may not be inherently neurodivergent, it's essential to recognize that individuals with neurodivergent conditions are not immune to depression. On the contrary, they may be at a higher risk due to factors such as social isolation, sensory sensitivities, difficulties in understanding and navigating social cues, and the pervasive stigma associated with neurodivergence (Mahjoob et al., 2023).
In fact, over my three decades of experience in mental health, I frequently see anxious individuals with comorbid neurodivergent conditions such as learning disabilities, ADHD, ASD, etc. often later have depression. Chronic worry can take a toll on a person’s brain and body and that can lead to a physical depression.
The intersection of depression and neurodivergence presents unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms of depression may overlap with those of neurodivergent conditions, leading to diagnostic complexities. Moreover, individuals with neurodivergent traits may require tailored approaches to therapy and support that address their specific needs and challenges.
Navigating Depression Treatment and Support
Regardless of whether depression occurs in neurotypical individuals or those who are neurodivergent, seeking appropriate treatment and support is paramount. Evidence-based therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), lifestyle modifications, and holistic interventions can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Healthcare providers must adopt a holistic and inclusive approach to mental health care to acknowledge the diverse experiences and needs of individuals across the neurodiversity spectrum. Cultivating empathy, understanding, and acceptance can foster a supportive environment where all individuals feel empowered to seek help and access the resources they need.
While depression itself may not be neurodivergent, its intersection with neurodivergent conditions highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing the diverse mental health needs within our communities.
Promoting awareness, advocacy, and inclusive practices, allows one to strive towards a more compassionate and supportive society for all individuals navigating the complexities of mental health.
Next Steps to Support a Neurodivergent Mood Disorder
Getting the right guidance to better understand depression and the neurodivergent brain is essential. When you understand how the brain works, it is easier to get to the right solutions to help your child or yourself self-regulate.

What does neurodivergent mean?
Experts define neurodivergent people as individuals whose brain functions and cognitive processes differ from the typical population. Neurodivergency covers a broad spectrum of conditions where variations in neurological development and functioning are observed. Neurodivergent brains don’t follow the typical patterns of brain structure and function.
What is neurodivergent depression?
Neurodivergent depression refers to depression experienced by individuals with conditions in the neurodivergent disorders list such as autism, ADHD, or dyslexia. It involves the presence of depressive symptoms within the context of existing neurodivergent traits in adults or kids, which can complicate diagnosis and treatment due to the unique challenges and needs associated with neurodivergence.
Is depression considered neurodivergent behaviors?
Depression itself is not typically considered a neurodivergent disability or behavior. The signs of being neurodivergent include having traits that may be more susceptible to depression. Understanding the different types of neurodivergence is essential for addressing the unique needs and challenges faced by individuals across the neurodiversity spectrum.
Is depression a neurological disorder?
Depression is often categorized as a psychiatric disorder rather than a neurological disorder, although it involves complex interactions between psychological, biological, and environmental factors. The definition of neurodivergent highlights the natural variations in brain functioning and cognitive processing among individuals. Neurodiverse people have neurological profiles and neurodivergent minds that function in a way described in the neurodivergence definition above.
Is bipolar neurodivergent?
Yes, bipolar disorder is often considered neurodivergent. Mental divergence encompasses a spectrum of neurological conditions. Aside from bipolar disorder, neurodivergent examples include conditions such as autism, ADHD, and dyslexia. Understanding the neurodivergent spectrum involves recognizing the diverse range of cognitive styles and experiences among individuals.
Is schizophrenia neurodivergent?
Yes, schizophrenia belongs is a condition under the neurodiversity umbrella, which involves a list of neurodivergencies. Neurodivergent conditions involve variations in brain structure, function, and cognitive processing compared to the neurotypical population.
What counts as neurodivergent autism?
A neurodivergent person with the autism neurotype means experiencing a diversity of cognitive functioning within the autism neurodiversity framework. This encompasses a broad range of cognitive styles, strengths, and challenges that characterize the autism and neurodiversity spectrum.
What disorders are neurodivergent?
The true meaning of neurodivergent disorders covers a range of conditions characterized by atypical brain functioning and cognitive processes. A neurodivergent diagnosis always comes with ASD, ADHD, dyslexia, dyspraxia, and Tourette syndrome, among others. These conditions differ from the typical nondivergent profile.
What falls under neurodivergent thinking?
A neurodiverse brain has a broad range of cognitive styles and approaches that diverge from the typical or neurotypical patterns of thought. It includes variations in problem-solving, perception, creativity, and information processing. It can also be seen in individuals with an acquired neurodivergent condition or a state of mentally divergent thinking.
How many people are neurodivergent individuals?
It is challenging to provide an exact number, but estimates suggest that a significant portion of the population may be neurologically divergent meaning they are non-neurotypical. Their neurodivergent tendencies encompass a wide spectrum of variations in cognitive processing and behavior.
Is neurodivergent a medical term?
Neurodivergent is not typically considered a medical term but rather a descriptive term used to denote individuals with neurally diverse cognitive profiles. Neurodivergent means exhibiting cognitive differences that differ from the typical or non divergent brain.
What is neurodivergence awareness?
Neurodivergence awareness recognizes the facts about neurodiversity, including the prevalence of undiagnosed neurodivergent individuals. For example, neurodivergence in women may present differently or be underdiagnosed compared to their male counterparts.
What are neurodivergent traits?
Neurodiverse conditions or traits encompass a wide array of characteristics and behaviors associated with all neurodivergent disorders, contributing to a neurodiverse character. A neurodiverse character exhibits differences in social interaction, communication, sensory processing, attention, and cognition.
What is neurodiversity coaching?
A neurodiversity coach provides support and guidance tailored to individuals with neurally divergent cognitive profiles, which cover a range of neurodivergent meanings. They focus on empowering clients to understand and leverage their unique strengths while addressing challenges associated with their cognitive differences.
Citations
Mahjoob, M., Paul, T., Carbone, J., Harshit Bokadia, Cardy, R. E., Kassam, S., Anagnostou, E., Andrade, B. F., Penner, M., & Azadeh Kushki. (2023). Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life in Neurodivergent Children: A Systematic Review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-023-00462-3
Mirowsky, J., & Ross, C. E. (1992). Age and Depression. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 33(3), 187. https://doi.org/10.2307/2137349
Dr. Roseann is a mental health expert in Neurodivergence who frequently is in the media:
- Healthline A 30-Minute Workout May Help Relieve Some Symptoms of Depression
- HealthCentral Summer Soothes Our Senses – and Our Souls
- The Healthy What Therapists Think About Neuro-Linguistic Programming for Mental Health
Always remember… “Calm Brain, Happy Family™”
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to give health advice and it is recommended to consult with a physician before beginning any new wellness regime. *The effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment vary by patient and condition. Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC does not guarantee certain results.
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about science-backed solutions, so you are in the right place!
Grab your complimentary copy of
147 Therapist-Endorsed Self-Regulation Strategies for Children: A Practical Guide for Parents
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Licensed Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including The Mel Robbins Show, CBS, NBC, PIX11 NYC, Today, FORBES, CNN, The New York Times, The Washington Post, Business Insider, Women’s Day, Healthline, CNET, Parade Magazine and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She coined the terms, “Re-entry panic syndrome” and “eco-anxiety” and is a frequent contributor to media on mental health.
Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge has three decades of experience in working with children, teens and their families with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism, concussion, dyslexia and learning disability, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), depression and mood disorder, Lyme Disease, and PANS/PANDAS using science-backed natural mental health solutions such as supplements, magnesium, nutrition, QEEG Brain maps, neurofeedback, PEMF, psychotherapy and other non-medication approaches.
She is the author of three bestselling books, It’s Gonna Be OK!: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child's Mental Health, The Teletherapy Toolkit, and Brain Under Attack. Dr. Roseann is known for offering a message of hope through science-endorsed methods that promote a calm brain.
Her trademarked BrainBehaviorResetⓇ Program and It’s Gonna be OK!Ⓡ Podcast has been a cornerstone for thousands of parents facing mental health, behavioral or neurodevelopmental challenges.
She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health, Neurotastic™Brain Formulas and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Mental Health Professional (CIMHP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2024










