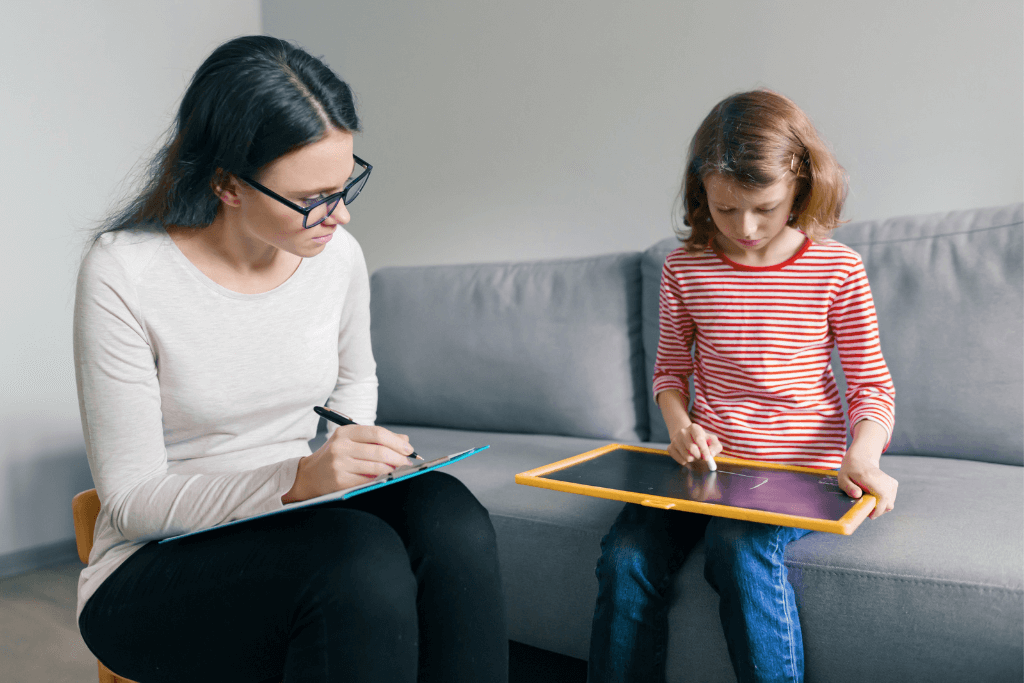
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder affects millions worldwide. As common as it is, ADHD can wreak havoc on a child's and family's life. It often impacts a person's ability to pay attention, control impulses, and manage behavior. It can also affect their academic and social functioning, leading to difficulties in their daily lives.
It leads to many stressful conversations at home about this assignment or that task not getting done (or maybe even started). At school, it may feel like a rollercoaster for a child. If your child is experiencing symptoms of ADHD, seek a professional evaluation. It can help determine whether ADHD is present and guide treatment options.
What is ADHD Testing?
ADHD testing is a necessary process that helps healthcare professionals determine whether one meets the diagnostic criteria for ADHD. It typically involves a series of assessments and evaluations to gather information about an ADHD kid's symptoms, history, and functioning.
The goal of ADHD testing is to identify symptoms consistent with ADHD and rule out other possible explanations for those symptoms. The types of tests used in ADHD testing may vary depending on the person's age and presenting symptoms.
What is it Like Being Tested for ADHD? What's the Process?
ADHD screening involves a series of assessments and evaluations to gather information about a child's symptoms, history, and functioning. The specific tests and procedures used during ADHD testing may vary depending on the child's age, symptoms, and other factors. Here are some steps involved in ADHD testing:
1. Initial Consultation
The testing process typically begins with an initial consultation with a healthcare practitioner specializing in diagnosing ADHD. During this consultation, the healthcare professional may gather information about the child's symptoms, medical history, educational history, and family history.
2. Gathering of Information
After the initial consultation, the healthcare professional may conduct a more in-depth assessment. They will gather additional information about your child's symptoms and functioning. It may involve collecting information from multiple sources, including individuals, family members, and teachers.
3. Testing Procedures
Depending on the child's age and presenting symptoms, the healthcare professional may use a variety of testing procedures to get the data they need. These procedures may include behavioral observations and rating scales that parents and teachers fill out. Sometimes individually administered standardized cognitive and academic assessments and rating scales are given too.
4. Feedback and Diagnosis
After the assessment or testing procedures are complete, the healthcare professional will provide the individual and their family feedback about the testing results. If ADHD is diagnosed, the healthcare professional may discuss treatment options.
How is ADHD Diagnosed Accurately?
An accurate diagnosis of ADHD requires the healthcare professional or specialist to collect information from multiple sources. Then evaluate the kid's behavior and symptoms in different settings. The American Academy of Pediatrics and American Psychiatric Association's diagnostic guidelines include the following:
1. Comprehensive Evaluation
A comprehensive evaluation should be conducted by a healthcare professional or specialist with experience diagnosing and treating ADHD.
2. Review of Medical and Family History
A review of the child's medical and family history can help identify any genetic or environmental factors that may contribute to ADHD symptoms.
3. Physical Exam
A physical exam can help rule out any underlying medical conditions contributing to ADHD symptoms.
4. Cognitive and Academic Assessments
Cognitive and academic assessments can help identify any cognitive deficits or learning disabilities related to ADHD.
5. Rating Scales
Rating scales are completed by the individual, parents, teachers, and other caregivers. They can provide valuable information about the child's behavior and symptoms in various settings. It is essential to understand how and where these issues impact a child.
6. Observation of Behavior
Direct observation of the kid's behavior in different settings can help confirm the presence of ADHD symptoms and rule out ADHD or other issues. Learning issues can resemble ADHD, and observation is a great way to see why your child isn't successful.
ADHD Testing Procedures
ADHD testing procedures typically involve a comprehensive evaluation process but may only include intake and rating scales. Our center also uses a QEEG brain map as part of our comprehensive intake process.
The goal is to accurately diagnose ADHD and develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the child's needs and symptoms.
Behavioral Observations
Behavioral observations are an essential part of ADHD testing and diagnosis. A healthcare professional or specialist may observe the kid at home, school, or clinically during a behavioral observation. They do so to assess the child's behavior and symptoms. Some common behaviors that may be observed during an ADHD assessment include:
1. Attention Problems
This test determines the symptoms of inattention in a child, including making careless mistakes, losing things, forgetfulness, and being easily distracted.
2. Hyperactivity
The child will be observed for behaviors such as fidgeting, restlessness, talking excessively, difficulty sitting still, and impulsivity.
3. Impulsivity
Testing for impulsivity may include an assessment to determine if the child is acting without thinking, interrupting others, and having difficulty waiting their turn.
Behavioral observations are important because they can help confirm the presence of ADHD and provide valuable information for developing an effective treatment plan.
In addition, by observing the child in different settings, the professional can understand their behavior and symptoms and how to support success. It helps them offer appropriate recommendations for ADHD treatment services and support at home and school.
Cognitive and Academic Assessments
Cognitive and academic assessments are commonly used in ADHD testing to evaluate a kid's cognitive abilities, academic performance, and potential learning disabilities. These assessments may include standardized tests and evaluations administered by a healthcare professional, school psychologist, or another ADHD specialist.
Cognitive assessments may include intelligence, memory, attention, and executive functioning tests. These tests can help identify any cognitive deficits contributing to a person's ADHD symptoms and any co-occurring learning disabilities.
Academic assessments may include tests of reading, writing, and math skills, along with academic performance and progress assessments. These tests can help identify any academic difficulties related to ADHD, such as problems with attention, organization, and time management.
Many children with ADHD struggle with reading comprehension and writing because their brains can't regulate enough to succeed in these tasks. It is essential to rule out dyslexia when a child with ADHD struggles with reading or writing.
Some common types of cognitive and academic assessments for ADHD include:

1. Intelligence Tests
These tests measure intellectual abilities, including verbal and nonverbal reasoning, problem-solving, and abstract thinking.
2. Memory Tests
Here, the test administrator evaluates an ADHD child's ability to remember and recall information, including short-term and long-term memory, and recall after a delay
3. Attention Tests
These tests measure a kid's ability to sustain attention and resist distractions.
4. Executive Functioning Tests
These tests evaluate the child's executive functions, such as the ability to plan, organize, initiate, and complete tasks, as well as their ability to regulate emotions and behavior.
5. Achievement Tests
These tests measure an ADHD child's academic skills and performance, including reading, writing, and math.
Cognitive and academic assessments can provide valuable information for developing an individualized treatment plan for ADHD. By identifying any cognitive deficits or academic difficulties, healthcare professionals and specialists can recommend appropriate interventions and accommodations. It helps children manage their symptoms and succeed academically.
ADHD Rating Scales
Rating scales are commonly used in ADHD testing to assess a child's behavior and symptoms in different settings. Rating scales are questionnaires completed by the individual, parents, teachers, and other caregivers who interact with the individual regularly. Some standard ADHD rating scales include:
1. Conners Rating Scales
These scales are widely used to assess ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents. They include parent and teacher versions that evaluate a range of behaviors, including hyperactivity, impulsivity, inattention, and emotional disturbance.
2. ADHD Rating Scale
This tool is also widely used and validated for assessing ADHD symptoms in children and adults. It includes questions about symptoms related to the symptoms of hyperactivity-impulsivity and inattention.
3. Behavior Assessment System for Children (BASC)
This comprehensive assessment tool includes rating scales completed by parents, teachers, and the individual being assessed. In addition, it evaluates a range of behaviors related to ADHD and emotional and behavioral problems.
4. Vanderbilt ADHD Diagnostic Rating Scale
Pediatricians commonly use this tool to assess ADHD symptoms in children. It includes questions about inattention, hyperactivity, impulsivity, academic performance, and social interaction.
Rating scales can provide valuable information about a kid's behavior and symptoms and help diagnose ADHD and monitor treatment progress. By gathering information from multiple sources, healthcare professionals can understand the child's behavior and symptoms. Doing so makes it easier for them to make appropriate recommendations for treatment and support.
How Much Does an ADHD Test Cost?
The cost of an ADHD test can vary depending on factors like testing type and the healthcare professional conducting the assessment. The cost of an ADHD test may include the cost of the evaluation or assessment and any cognitive or academic assessments administered. It also includes rating scales or other tests to evaluate symptoms and behavior.
The cost of an ADHD evaluation or assessment may range from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars, with a few thousand dollars being more typical for a full psychoeducational or neuropsychological evaluation.
Insurance coverage may vary depending on the policy of the ADHD patient and the healthcare provider. Some insurance plans may cover part or all of the cost of testing.
Who Conducts ADHD Testing?
Mental health professionals typically conduct ADHD testing with specialized training in assessing and diagnosing ADHD. The specific type of professional who performs ADHD testing may vary depending on the child's age, symptoms, and other factors. Here are some healthcare professionals who may conduct ADHD testing:
1. Psychologists and Neuropsychologists
Psychologists are healthcare professionals who specialize in assessing, diagnosing, and treating mental health issues. Many psychologists have specialized training in evaluating ADHD. They may conduct various assessments, including behavioral observations, cognitive and academic assessments, and rating scales.
2. Psychiatrists
Psychiatrists specialize in treating mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may conduct ADHD testing and prescribe ADHD medication if a formal diagnosis is made.
3. Neurologists
Neurologists specialize in diagnosing and treating neurological conditions affecting the brain and nervous system. Some neurologists may have specialized training in assessing ADHD and may conduct ADHD testing.
4. Other Healthcare Professionals
Other professionals who may conduct ADHD testing include a primary care provider, nurse practitioner, and physician assistant. These health professionals may refer individuals to specialists for further testing or treatment if ADHD is suspected.
Importance of Seeking Professional Help

A proper diagnosis is crucial to identify and treat ADHD effectively. We often minimize the impact of ADHD on children’s lives because these kids are typically so bright, but it can devastate a child and their family life.
Only a trained professional can diagnose ADHD accurately and rule out other conditions that may mimic ADHD symptoms. Seeking professional help can provide emotional support, education, and resources for children and their families. It also reduces the negative impact of ADHD on their lives. Seeking professional help for ADHD is essential for several reasons:
1. Accurate ADHD Diagnosis
A professional specializing in assessing and diagnosing ADHD can provide an accurate diagnosis, which is essential for effective treatment. ADHD can have symptoms that overlap with other conditions. A professional evaluation is necessary to rule out other possible causes, including dyslexia, learning disability, brain injury or concussion, anxiety, OCD, mood disorder, and PANS/PANDAS.
2. Individualized Treatment Plan
Once a diagnosis is made, the professional can develop an individualized treatment plan based on the child's unique symptoms, needs, and goals. In our BrainBehaviorReset™ Program, we develop a customized care plan designed to support the brain and behavior. For example, treatment for ADHD may involve behavioral therapy, neurofeedback, PEMF, executive functioning coaching, or a combination of these.
We can help determine the best course of treatment based on your child’s individual needs after we do an intake with a QEEG brain map.
3. Improved Functioning
Treatment for ADHD can improve the child's functioning in multiple areas, including academic and home life, social relationships, and overall quality of life. The professional you work with can help monitor progress and adjust the treatment plan. We use multiple measures to monitor progress, including brain maps and custom symptom trackers that can show which behaviors are changing.
4. Support and Guidance
ADHD can be challenging to manage, and individuals with ADHD may benefit from additional support and guidance. A mental health professional can educate and support individuals and their families, helping them understand the condition and manage the associated symptoms.
It is essential to understand that your child isn’t doing this on purpose, which starts with understanding the brain. Once you understand how ADHD affects the brain and behavior, you can better shape desired behaviors.
5. Co-occurring Conditions
ADHD often co-occurs with other conditions, such as learning disabilities, anxiety disorder, or depression. Your evaluator or provider can identify and rule these co-occurring conditions in or out. Without looking at if it is ADHD or something else, then you really can’t get the proper treatment plan.
Preparing for ADHD Testing
If your child is scheduled for ADHD testing, there are several things you can do to prepare for the process. Here's how:
1. Gather information
Before the testing process begins, gather as much information as possible about the child's symptoms, medical history, and educational history. It may include reports from previous evaluations and medical and school records.
2. Discuss Expectations with the Evaluator
Talk to the mental health professional conducting the testing about what to expect during the process. Ask questions about the tests and procedures used and how long the testing process will likely take. Also, ask how they would like the testing explained to your child.
3. Follow the Instructions
The evaluator may provide specific instructions before the testing begins, such as avoiding caffeine or certain medications. They may ask to bring snacks or to go to bed early. Make sure to follow these instructions carefully.
4. Be Honest
During the testing process, be honest about any symptoms or concerns you or your loved one may be experiencing. If you don’t lay your cards on the table, your child can’t get the help they need. It will help the evaluator make an accurate diagnosis, hopefully leading to a good care plan
5. Prepare for Behavioral Observations
If the testing process includes behavioral observations, inform the evaluator about the child’s typical behavior at home and school. Make sure you have the proper consent for school observation, and ideally, the observation should occur before he or she meets your child.
6. Plan for Breaks
The testing process can be lengthy and involve several tests and procedures. Plan for breaks during the process to help the individual stay focused and engaged. When I did psychoeducational testing, I broke testing up over five or six days to get a more accurate picture of the child’s cognitive potential.
7. Stay Positive
Feeling anxious or nervous about the testing process is natural. However, try to stay positive and remember that the goal of ADHD testing is to help identify any issues. You also want to use positive language with your child when explaining testing because they look to you to set the tone.
Ultimately a thorough evaluation should provide the path to appropriate treatment and support. If you are looking for guidance on how to help your child thrive, apply to work with us.
Always remember… “Calm Brain, Happy Family™”
Are you looking for SOLUTIONS for your struggling child or teen?
Dr. Roseann and her team are all about solutions, so you are in the right place!
There are 3 ways to work with Dr. Roseann:
You can get her books for parents and professionals, including: It’s Gonna Be OK™: Proven Ways to Improve Your Child’s Mental Health, Teletherapy Toolkit™ and Brain Under Attack: A Resource For Parents and Caregivers of Children With PANS, PANDAS, and Autoimmune Encephalopathy.
If you are a business or organization that needs proactive guidance to support employee mental health or an organization looking for a brand representative, check out Dr. Roseann’s media page and professional speaking page to see how we can work together.
Dr. Roseann is a Children’s Mental Health Expert and Therapist who has been featured in/on hundreds of media outlets including, CBS, NBC, FOX News, PIX11 NYC, The New York Times, The Washington Post,, Business Insider, USA Today, CNET, Marth Stewart, and PARENTS. FORBES called her, “A thought leader in children’s mental health.”

She is the founder and director of The Global Institute of Children’s Mental Health and Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge. Dr. Roseann is a Board Certified Neurofeedback (BCN) Practitioner, a Board Member of the Northeast Region Biofeedback Society (NRBS), Certified Integrative Medicine Mental Health Provider (CMHIMP) and an Amen Clinic Certified Brain Health Coach. She is also a member of The International Lyme Disease and Associated Disease Society (ILADS), The American Psychological Association (APA), Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) National Association of School Psychologists (NASP), International OCD Foundation (IOCDF) International Society for Neurofeedback and Research (ISNR) and The Association of Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback (AAPB).
© Roseann-Capanna-Hodge, LLC 2023
Disclaimer: This article is not intended to give health advice and it is recommended to consult with a physician before beginning any new wellness regime. *The effectiveness of diagnosis and treatment vary by patient and condition. Dr. Roseann Capanna-Hodge, LLC does not guarantee certain results.